Research and Articles
Hotline
- Capital Markets Hotline
- Companies Act Series
- Climate Change Related Legal Issues
- Competition Law Hotline
- Corpsec Hotline
- Court Corner
- Cross Examination
- Deal Destination
- Debt Funding in India Series
- Dispute Resolution Hotline
- Education Sector Hotline
- FEMA Hotline
- Financial Service Update
- Food & Beverages Hotline
- Funds Hotline
- Gaming Law Wrap
- GIFT City Express
- Green Hotline
- HR Law Hotline
- iCe Hotline
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Hotline
- International Trade Hotlines
- Investment Funds: Monthly Digest
- IP Hotline
- IP Lab
- Legal Update
- Lit Corner
- M&A Disputes Series
- M&A Hotline
- M&A Interactive
- Media Hotline
- New Publication
- Other Hotline
- Pharma & Healthcare Update
- Press Release
- Private Client Wrap
- Private Debt Hotline
- Private Equity Corner
- Real Estate Update
- Realty Check
- Regulatory Digest
- Regulatory Hotline
- Renewable Corner
- SEZ Hotline
- Social Sector Hotline
- Tax Hotline
- Technology & Tax Series
- Technology Law Analysis
- Telecom Hotline
- The Startups Series
- White Collar and Investigations Practice
- Yes, Governance Matters.
- Japan Desk ジャパンデスク
Regulatory Hotline
July 20, 2022RBI Allows International Trade Settlements in Indian Rupees
Introduction
In its attempt to promote global trade, the Reserve Bank of India (“RBI”), vide its notification1, dated July 11, 2022, has come up with the International Trade Settlement in Indian Rupees mechanism (“ITSIR Mechanism”) for the purposes of invoicing, payment and settlement of exports / imports in Indian Rupees (“INR”).
What does ITSIR Mechanism entail?
Under the ITSIR Mechanism, the overseas bank of the foreign party, with whom Indian exporter / importer is dealing, would open a Special Rupee Vostro account2 (“Vostro Account”) with an Authorised Dealer bank (“AD bank”) in India, for which the AD bank would be required to procure RBI’s permission. Post receiving RBI’s blessings, the Indian exporter and importer would be able to raise and receive invoices in INR, respectively, with the option to use the market prevailing currency exchange rate for the transaction.
The settlement of trade under the ITSIR Mechanism would happen in the following manner:
-
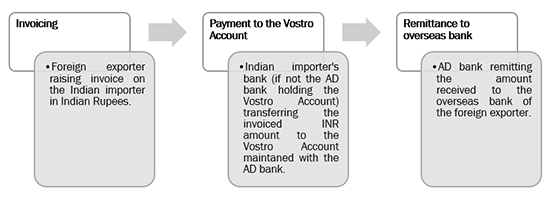
Import: Foreign exporter would raise an invoice in INR on the Indian importer. The Indian importer would instruct its Indian bank to transfer the invoiced INR amount to the Vostro Account maintained with the AD bank. Thereafter, the AD bank would remit the invoiced INR amount to the overseas bank of the foreign exporter.
-
Export:. Indian exporter would raise an invoice in INR on the overseas importer. The export proceeds would be paid out of the balances in the Vostro Account maintained with the AD bank. The AD bank would transfer the invoiced INR amount to the Indian bank of the Indian exporter.
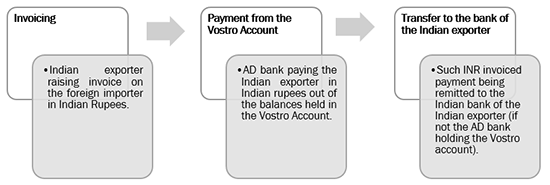
Thus, the debit and credit of the Vostro Account would represent the trade occurring between India and the participating nation.
Features of ITSIR Mechanism
The introduction of the ITSIR Mechanism can prove to be more efficient and an easier way to trade with India. To stimulate the adoption of this mechanism, the RBI has not only shied away from saddling the parties with additional substantive and procedural responsibilities, but also has prescribed further relaxations. The prescribed features of the ITSIR Mechanism are as under:
-
The export / import undertaken and settled under the ITSIR Mechanism would not be subject to additional documentation and reporting requirements. The usual documentation of a Letter of Credit (“LC”) and agreed documents as per the Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (“UCPDC”) and Incoterms3 would suffice.
-
Indian exporters would be permitted to receive advance payment against exports, provided that:
-
the available funds in the Vostro Accounts should first be used towards payment of executed export orders and export payments due; and
-
the claim of the exporter should be verified by the AD bank with the advice received from the correspondent bank before releasing the advance.
-
-
In case of foreign entity acting as both, a buyer and a supplier, export receivables may be set-off against import payables, subject to the conditions prescribed in the Master Direction on Export of Goods and Services, 2016, as amended from time to time.4
-
Export / import undertaken and settled under the ITSIR Mechanism shall be supportable by bank guarantees, subject to provisions of Foreign Exchange Management (Guarantees) Regulations, 20005 and the Master Circular on Guarantees and Co-acceptances, 20156, as amended from time to time.
-
Pursuant to mutual agreement between the parties, the surplus balance in the Vostro Account could be used for:
-
Payments for projects and investments;
-
Export/import advance flow management; and
-
Investment in Government Treasury Bills, Government securities, etc. in terms of applicable Indian laws.
-
Takeaways
The RBI, by notifying the ITSIR Mechanism, seems to be inching closer to making INR a globally acceptable currency for trade settlement as opposed to the US Dollar (“USD”). Under the present system, the settlement of international trade between India and any other country happens in USD, granting USD a global reserve currency status. However, this process exposes Indian traders to foreign exchange rate fluctuations and currency conversion expenses. The ITSIR Mechanism, which calls for trade settlement in INR, should, in the long run, make INR a globally acceptable currency and reduce India’s dependency on USD.
Further, in light of India’s persisting trade deficit, settling international trade in INR should also save USD outflows shoring up India’s foreign exchange reserves, which has considerably reduced in the last 2-3 weeks7. This step also hints towards facilitating trades with certain countries facing financial and economic hurdles.
You can direct your queries or comments to the authors
1 RBI notification RBI/2022-2023/90, available at
https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/NotificationUser.aspx?Id=12358&Mode=0
2 A Rupee Vostro account is a foreign bank’s account with an Indian bank in rupees in India. Also, the AD bank would need to ensure that the correspondent bank is not from a jurisdiction in the updated FATF Public Statement on High Risk & Non Co-operative Jurisdictions on which FATF has called for counter measures.
3 International Commercial Terms.
4 Paragraph C.26 on ‘Set-off of export receivables against import payables’ under RBI Master Direction – Export of Goods and Services, 2016, available at
https://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/BS_ViewMasDirections.aspx?id=10395
5 Foreign Exchange Management (Guarantees) Regulations, 2000, Notification No. FEMA 8/2000-RB, available at
https://rbi.org.in/Scripts/BS_FemaNotifications.aspx?Id=162
6 RBI Master Circular - Guarantees and Co-acceptances, 2015, available at
https://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/BS_ViewMasCirculardetails.aspx?id=5130
7 India's foreign exchange reserves stand at $580.252 billion as on July 8, 2022, as per the Reserve Bank of India's Weekly Statistical Supplement, dated July 15, 2022, available at
https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/Wss/PDFs/2T_1507202258970629D61D4B

